Dr Manish Singhal - The best Cancer Specialist in Delhi
Cervical Cancer Specialist in Noida, Delhi NCR
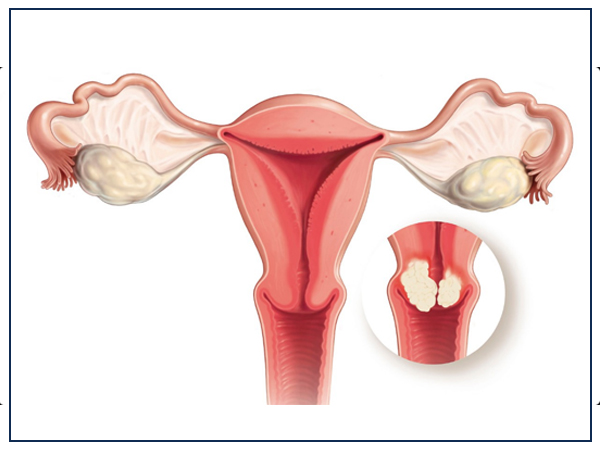
Everything You Need To Know About Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is the term used to depict tumors that can develop at the lower end of the womb. These tumors typically create from anomalous cell changes at the passageway to the womb from the vagina (the opening of the cervix). Irregular cell changes can be recognized through screening and after that expelled. An immunization against infections that reason growth (HPV antibody) can diminish the danger of cervical disease. The cervix (neck of the womb) is a solid, strong tube-like structure. The exceptionally base end of the cervix stands out into the vagina a bit, at the opening of the cervix. Within the cervix is fixed with a mucous layer. Organs in the mucous film create a thick fluid (cervical bodily fluid) that goes about as an obstruction, keeping germs from entering the womb from the vagina.
Most cervical cancers (80 to 90 percent) are squamous cell tumors. Adenocarcinoma is the second most normal sort of cervical cancer, representing the rest of the 10 to 20 percent of cases. Adenocarcinoma creates from the organs that deliver bodily fluid in the endocervix. While less regular than squamous cell carcinoma, the frequency of adenocarcinoma is on the ascent, especially in younger women.
Cervical cancer is the second most common tumor for ladies around the world, but since it creates after some time, it is additionally a standout amongst the most preventable sorts of disease.Cancer of the cervix has a tendency to happen amid midlife. Half of the ladies determined to have the infection are in the vicinity of 35 and 55 years old. It once in a while influences ladies under age 20, and around 20 percent of judgments are made in ladies more seasoned than 65. Consequently, it is imperative for ladies to proceed cervical cancer screening until at any rate the age of 70.
There are several treatment plans for cervical cancer patients, even during the Covid-19 pandemic. Some oncologists are altering treatment plans, and some are postponing treatment. Dr. Manish Singhal , the best cancer specialist in Delhi NCR and Oncologist in Noida and his team are taking a different route by providing cancer care services while maintaining safety measures including chemotherapy at home, video consultation, online check-in, and more. Dr. Singhal is trusted by thousands of patients for the best treatment on Cervical Cancer in Noida.
Know the Risk Factors
A risk factor is anything that expands a person’s shot at creating cancer. In spite of the fact that risk factors frequently impact the improvement of cancer, most don’t straightforwardly cause disease. A few people with a few risk factors never create cancer, while others with no known risk factors do. Knowing your risk actors and discussing them with your specialist may enable you to make a more educated way of life.
The following elements below may raise a danger of creating cervical cancer :
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
The most common reason for the cervical cancer is infection with HPV. Research demonstrates that cancer with this infection is a risk factor for cervical tumor. Sexual action with somebody who has HPV is the most well-known way somebody gets HPV. There are more than 100 distinct sorts of HPV, not which are all connected to cancer. The HPV types that are most every now and again connected with the cervical cancer are HPV16 and HPV18.
Immune system deficiency
Ladies with the lowered immune system have a higher danger of creating cervical cancer. A lowered immune system can be caused by immune suppression from corticosteroid prescriptions, organ transplantation, medications for different kinds of cancer, or from the human immunodeficiency infection (HIV), which is the infection that causes (AIDS). At the point when a lady has HIV, her immune system is less ready to ward off early growth.
Herpes
Women who have genital herpes have a higher danger of having cervical cancer.
Smoking
Ladies who smoke are twice as liable to create cervical cancer as ladies who don’t smoke.
Age
Girls who are 15 years old or younger rarely create cervical cancer. The risk goes up between the late youngsters and mid-30s. Ladies more than 40 years old stay in danger and need to keep having standard cervical tumor screenings, which incorporate both a Pap test and HPV test.
Financial components
A cervical cancer is more typical among gatherings of ladies who are less inclined to approach screening for cervical cancer.
Oral contraceptive
Some researchers suggest that oral contraceptives, which are conception prevention pills, might be related to an expansion in the danger of cervical cancer. Be that as it may, more research is expected to see how oral preventative utilizes and the advancement of cervical cancer are associated.
Exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES)
Ladies whose moms were given this medication amid pregnancy to avoid unsuccessful labor have an expanded danger of building up an uncommon kind of disease of the cervix or vagina. DES was given for this reason from around 1940 to 1970. Ladies presented to DES ought to have a yearly pelvic examination that incorporates a cervical Pap test and in addition a 4-quadrant Pap test, in which tests of cells are taken from all sides of the vagina to check for strange cells.
Research keeps on investigating what factors cause this sort of cancer and what ladies can do to bring down their own risk. There is no demonstrated method to totally keep this illness, yet there might be steps you can go for broke to bring down your disease chance. Talk to your specialist if you have worries about your own danger of building up this sort of cancer.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
In many cases, cervical cancer does not cause detectable side effects in the beginning periods of the illness. Routine Pap screening is vital to check for unusual cells in the cervix, so they can be observed soon and regarded as right on time as could be expected under the circumstances.
Following are the regular side effects of cervical cancer:
-
Vaginal bleeding:
This incorporates seeping between periods, after sex or post-menopausal bleeding.
-
Irregular vaginal release:
A watery, pink or noxious release is normal.
-
Pelvic pain:
Pain during intercourse or at different circumstances might be an indication of unusual changes to the cervix or less genuine conditions. Cervical cancer may spread (metastasize) inside the pelvis, to the lymph hubs or somewhere else in the body. Following are the advanced symptoms of cervical cancer. Contact a doctor if you see any of those.
- Sudden weight loss
- Back pain
- Leg pain or swelling
- Leakage of urine or feces from the vagina
- Bone fractures
Stages
Specialists appoint the phase of the disease by assessing the tumor and whether cancer has spread to lymph hubs and different parts of the body. These are the following stages
The tumor has spread from the cervix lining into the more profound tissue yet is still simply found in the uterus. It has not spread to lymph hubs or different parts of the body. This stage might be depicted in more detail (see beneath).
The cancer is analyzed just by microscopy, which is seeing cervical tissue or cells under a magnifying instrument. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no far off spread.
There is a carcinogenic zone of 3 millimeters (mm) or littler top to bottom and 7 mm or little longer. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no removed spread.
There is a carcinogenic zone bigger than 3 mm yet not bigger than 5 mm top to bottom and 7 mm or little longer. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no removed spread.
In this stage, the specialist can see the injury, and the disease is discovered just in the cervix. Or then again there is an injury that can be seen utilizing a magnifying instrument, and it is bigger than a phase IA2 tumor. The growth may have been found through a physical examination, laparoscopy, or another imaging strategy. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no removed spread.
The tumor is 4 centimeters (cm) or littler. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no far off spread.
The tumor is bigger than 4 cm. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no removed spread.
The tumor has spread past the cervix to close-by territories, for example, the vagina or tissue close to the cervix, yet it is still inside the pelvic territory. It has not spread to lymph hubs or different parts of the body. This stage might be portrayed in more detail.
The tumor has not spread to the tissue beside the cervix, additionally called the parametrial territory. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no far off spread.
The tumor is bigger than 4 cm. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no distant spread.
The tumor has spread to the parametrial zone. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no distant spread.
The tumor is 4 cm or littler. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no distant spread.
The tumor has spread to the pelvic divider, or potentially includes the lower third of the vagina, as well as causes swelling of the kidney, called hydronephrosis, or prevents a kidney from working. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no distant spread.
The tumor includes the lower third of the vagina, however, it has not developed into the pelvic divider. No lymph hubs are included, and there is no removed spread.
The tumor has developed into the pelvic divider and additionally influences the kidney, however, it has not spread to the lymph hubs or far off destinations. Or then again, cancer has spread to lymph hubs in the pelvis, yet not inaccessible destinations and the tumor can be any size.
The disease has spread to the bladder or rectum and could conceivably have spread to the lymph hubs, yet it has not spread to different parts of the body.
Tests and Screenings
The following are the tests and procedures for cervical cancer
Bimanual pelvic exam
In this examination, the specialist will check a lady’s body for any bizarre changes in her cervix, uterus, vagina, ovaries, and other close-by organs. In the beginning, the specialist will search for any progressions to the lady’s vulva outside the body and after that, utilizing an instrument called a speculum to keep the vaginal dividers open, the specialist will glimpse inside the lady’s body. A portion of the adjacent organs are not obvious during this exam, so the specialist will then embed 2 fingers of 1 hand inside the patient’s vagina while the other hand tenderly pushes on the lower midriff to feel the uterus and ovaries. This exam normally takes a couple of minutes and is done in an examination room.
HPV test
This test is done on an example of cells expelled from the lady’s cervix, a similar example utilized for the Pap test. This sample is tried for the strains of HPV most usually connected to cervical cancer. HPV testing might be finished without anyone else’s input or joined with a Pap test. This test may likewise be done on an example of cells gathered from a lady’s vagina, which she can gather herself.
Pap test
The Pap test has been the most well-known test for early changes in cells that can prompt cervical tumor. This test is additionally called a Pap smear. A Pap test includes gathering a sample of cells from the cervix. It is frequently done in the meantime as a bimanual pelvic exam. A Pap test might be joined with HPV test.
Visual inspection with acetic acid (VIA)
VIA is a screening test that should be possible with few instruments and the stripped eye. During VIA, a weakening of white vinegar is connected to the cervix. A health care at that point searches for variations from the norm on the cervix, which will turn white when presented with vinegar. This screening test is extremely valuable in places where access to therapeutic care is constrained.
All ladies get no less than 1 HPV test to screen for cervical cancer in their lifetime. Ladies with 25 to 65 years of age ought to get a screening with the HPV test at regular intervals. Ladies who are 65 and more established may quit screening if their HPV test comes about have been generally negative over the past 15 years. Ladies who are 65 and more seasoned and who have tried positive for HPV may keep screening until the point when they are 70.
Choices about screening for cervical cancer are ending up progressively individualized. Sometimes, screening may differ from the recommendations discussed above because of a variety of factors. Such factors incorporate the accessibility of testing and follow-up choices in your general vicinity, your own risk factors, and your health history. It’s critical to chat with a Cancer doctor about how regularly you ought to get screening and which tests are most appropriate.n places where access to remedial care is constrained.
Prevention
Cervical cancer can frequently be counteracted by having normal screenings to discover any precancers and treat them. Preventing precancers implies controlling conceivable risk factors, for example,
- Delaying the first intercourse until the late teens
- Constraining the quantity of sex partners
- Maintaining a strategic distance from sex with individuals who have had many partners
- Dodging sex with individuals who are clearly contaminated with genital warts or show different indications
- Quitting smoking
- Get vaccinated
Vaccines are accessible that can secure youngsters against certain HPV infections. These immunizations secure against infection with the HPV subtypes most regularly connected to cancer, and also a few sorts that can cause butt-centric and genital warts.
These vaccines just work to forestall HPV infections − they won’t treat the disease. That is the reason, the HPV antibodies ought to be given before a person ends up noticeably presented to HPV (for example, through sexual activity).
Cervical cancer executes approximately 67,477 Indian ladies every year. The two HPV vaccines right now accessible in India are bivalent (Cervarix, Rs 2190 for every measurement) and quadrivalent (Gardasil, Rs 3000 for every dosage.) TheNonavalent, which is thought to be the best in the West, is greatly costly and at present, not accessible in India as it is as yet not endorsed by the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI).



